Health
Seitan Recipes: The Ultimate Guide for Delicious Plant-Based Cooking

Introduction
What are seitan recipes and what do they offer? Simply put, seitan recipes are creative, flavorful dishes made using seitan — a protein-rich meat substitute crafted from wheat gluten. Unlike tofu or tempeh, seitan has a chewy, meat-like texture that makes it a popular choice for vegans, vegetarians, and anyone looking to reduce meat consumption without sacrificing taste or satisfaction. Seitan recipes offer versatility, allowing you to recreate everything from savory stir-fries and hearty sandwiches to BBQ ribs, curries, and even holiday roasts. With the right techniques, you can turn this humble ingredient into mouthwatering meals that please both plant-based eaters and meat lovers alike.
1. Background and Evolution of Seitan
Seitan originated in East Asia centuries ago, most notably in China and Japan, where Buddhist monks used it as a staple protein source. Known as “wheat meat” or “gluten,” it became a popular alternative to animal protein in vegetarian diets. Over time, seitan gained global attention as plant-based eating grew more mainstream. Today, seitan recipes are found in modern kitchens, vegan restaurants, and packaged ready-to-eat meals worldwide.
2. Key Features of Seitan
Here are some key characteristics of seitan that make it ideal for recipes:
-
High protein content – Roughly 21 grams of protein per 100 grams.
-
Chewy, meat-like texture – Closely mimics beef, chicken, or pork.
-
Versatility – Can be grilled, fried, baked, braised, or stewed.
-
Neutral flavor – Absorbs marinades and seasonings easily.
-
Customizable – Can be shaped into cutlets, strips, chunks, or loaves.
3. Detailed Explanations of Each Feature
High Protein Content
Seitan is one of the highest plant-based protein sources, often surpassing tofu or legumes. This makes seitan recipes especially beneficial for athletes and those aiming to meet daily protein needs without animal products.
Meat-Like Texture
Unlike tofu’s softness, seitan’s fibrous texture is ideal for replicating dishes like steak, kebabs, or stir-fry beef. Its chewiness provides a satisfying bite similar to real meat.
Versatility in Cooking
From pan-fried cutlets to slow-cooked curries, seitan adapts to a variety of cooking methods. Recipes can transform it into smoky BBQ ribs, crispy nuggets, or savory stews.
Flavor Absorption
Seitan naturally has a mild taste, allowing marinades, sauces, and spices to shine. Whether you prefer Asian-inspired soy marinades or spicy Tex-Mex flavors, seitan recipes can be customized easily.
4. Popular Types of Seitan Recipes
Some of the most loved seitan dishes include:
-
Seitan stir-fry with vegetables and soy sauce
-
BBQ seitan ribs glazed with smoky sauce
-
Seitan gyros or shawarma wrapped in pita bread
-
Seitan curry with coconut milk and spices
-
Seitan roast for festive occasions
-
Seitan “chicken” nuggets breaded and fried
5. Comparisons: Seitan vs. Other Meat Alternatives
| Feature | Seitan | Tofu | Tempeh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Very high | Moderate | High |
| Texture | Chewy, meat-like | Soft, spongy | Firm, nutty |
| Flavor absorption | Excellent | Good | Mild, earthy |
| Gluten content | High (not gluten-free) | Gluten-free | Gluten-free |
6. Benefits of Seitan for Different Types of Eaters
-
Vegans & Vegetarians: A satisfying protein substitute.
-
Athletes: High-protein, low-fat source for muscle recovery.
-
Flexitarians: Easy way to cut back on meat while enjoying familiar textures.
-
Families: Versatile enough for kid-friendly dishes like nuggets or tacos.
7. Nutritional Value, Health, and Safety Considerations
Seitan is nutrient-dense, offering protein, iron, and selenium. However, it is not suitable for those with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. As with any processed food, moderation is key — especially when buying pre-packaged seitan with added sodium or flavorings.
8. Future Trends in Seitan-Based Cooking
As plant-based diets grow, seitan recipes continue to evolve. Expect to see:
-
More ready-to-eat seitan products in grocery stores.
-
Fusion recipes blending global cuisines.
-
Health-focused innovations with fortified nutrients.
-
Gluten-free alternatives mimicking seitan’s texture.
9. Cost of Making or Buying Seitan
-
Homemade seitan: Inexpensive; a bag of vital wheat gluten makes multiple servings.
-
Store-bought seitan: Typically $4–$8 per package, depending on brand and flavor.
10. Pros and Cons of Seitan Recipes
Pros:
-
Excellent protein source
-
Realistic meat texture
-
Versatile in cooking styles
-
Affordable to make at home
Cons:
-
Not gluten-free
-
Lower in essential amino acids compared to soy
-
Store-bought versions may contain additives
11. Final Conclusion: Are Seitan Recipes Worth It?
Yes — seitan recipes are absolutely worth trying, especially for those seeking satisfying, high-protein meals without animal products. While not suitable for gluten-intolerant individuals, seitan provides a meat-like experience that makes plant-based eating more enjoyable and accessible.
12. FAQs about Seitan Recipes
1. What is seitan made of?
Seitan is made from vital wheat gluten, the main protein in wheat.
2. Is seitan healthier than meat?
It depends — seitan is lower in fat and cholesterol-free but doesn’t offer the same amino acid profile as meat.
3. Can I make seitan at home?
Yes, with vital wheat gluten, water, and seasonings, you can easily prepare it in your kitchen.
4. Is seitan gluten-free?
No, it’s made entirely from gluten and is unsuitable for celiac disease patients.
5. How long does homemade seitan last?
Stored in the fridge, it lasts about 5–7 days, or you can freeze it for longer.
6. Can I grill seitan?
Absolutely! Seitan grills beautifully and holds marinades well, making it perfect for BBQs.
Health
The Best Cycle Trainer: Transform Your Indoor Riding Experience

Indoor cycling has evolved into a serious training solution for fitness lovers, commuters, and competitive riders. A modern cycle trainer lets you ride anytime, regardless of weather, traffic, or daylight. It turns a regular bicycle into a powerful indoor workout machine that builds endurance, strength, and consistency.
This guide explains everything you need to know, from core types and resistance systems to noise levels and training goals. It is written from real-world riding experience, current product behavior, and hands-on evaluation standards used by serious cyclists today.
Why Indoor Cycle Training Matters Today
Indoor training is no longer a backup option. It is a primary tool for structured fitness. Riders use it to maintain routine, track progress, and train safely at home. With proper setup, indoor cycling improves cadence control, power output, and cardiovascular health faster than unstructured outdoor rides.
Many riders choose the Best Cycle Trainer because it delivers predictable resistance, repeatable workouts, and measurable improvement without distractions.
Types of Cycle Trainers Explained Clearly
Understanding trainer types helps you avoid wasting money and ensures the right fit for your goals.
1. Wheel-On Trainers
These trainers clamp onto the rear wheel. Resistance presses against the tire.
Pros
- Affordable
- Lightweight
- Easy to store
Cons
- Tire wear
- Slightly louder
- Less precise resistance
2. Direct-Drive Trainers
The rear wheel is removed. The bike mounts directly onto the trainer cassette.
Pros
- Very quiet
- Accurate resistance
- No tire damage
Cons
- Higher cost
- Heavier
3. Roller Trainers
The bike sits freely on rolling drums.
Pros
- Improves balance
- Natural road feel
Cons
- Steep learning curve
- Not ideal for high resistance workouts
Resistance Systems That Matter
Resistance defines workout quality. These are the main systems used today.
Magnetic Resistance
Simple and durable. Best for casual riders.
Fluid Resistance
Smooth and progressive. Popular for realistic road feel.
Electromagnetic Resistance
Digitally controlled. Ideal for structured training plans and interval work.
Noise Levels and Home Comfort
Noise is a major factor for apartment riders and shared spaces. Direct-drive models are the quietest. Wheel-on trainers create more vibration but remain manageable with a mat. Proper setup, tire choice, and surface padding reduce sound significantly.
Stability, Safety, and Bike Compatibility
A good trainer stays solid during sprints and climbs. Look for:
- Wide base footprint
- Non-slip feet
- Adjustable axle support
Compatibility matters. Modern trainers support road, gravel, and mountain bikes with standard axle adapters. Always confirm axle type before purchase.
Training Accuracy and Performance Tracking
Accurate resistance helps measure improvement. Advanced trainers respond instantly to cadence changes and maintain steady output. This precision makes indoor cycling effective for:
- Weight loss
- Endurance training
- Rehabilitation
- Power-based workouts
This is where the Best Cycle Trainer separates itself from entry-level options.
Comparison Chart: Choosing the Right Trainer
| Feature | Wheel-On | Direct-Drive | Rollers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noise Level | Medium | Very Low | Low |
| Resistance Accuracy | Moderate | High | Low |
| Setup Time | Fast | Moderate | Moderate |
| Tire Wear | Yes | No | No |
| Price Range | Low | High | Medium |
| Skill Required | Beginner | Beginner | Advanced |
This chart helps you match trainer type with lifestyle, budget, and experience.
Setup Tips for Better Results
Correct setup improves comfort and prevents injury.
- Use a level surface
- Install a sweat guard
- Adjust saddle height carefully
- Warm up before intense sessions
- Cool down after every ride
Small adjustments make indoor rides feel natural and sustainable.
Maintenance and Longevity
A quality trainer lasts years with minimal care.
- Clean after sweaty sessions
- Tighten bolts monthly
- Store in dry conditions
- Check resistance unit annually
Well-maintained trainers stay smooth and reliable over time.
Who Should Use Indoor Cycle Trainers?
Indoor trainers benefit many people:
- Busy professionals
- Parents with limited time
- Athletes training consistently
- Beginners building confidence
- Riders avoiding traffic risks
With the right choice, indoor cycling fits almost every lifestyle.
How to Choose with Confidence
Before buying, ask yourself:
- How quiet does it need to be?
- Do I want structured workouts?
- What bike do I own?
- How much space do I have?
- What is my training goal?
Answering these questions narrows options fast and prevents regret.
FAQs
Is indoor cycling effective for weight loss?
Yes. Consistent indoor rides burn calories efficiently and support fat loss when paired with good nutrition.
How often should I use a cycle trainer?
Three to five sessions per week delivers strong fitness results without overtraining.
Do trainers damage bicycles?
No. Proper installation and maintenance keep bikes safe and aligned.
Can beginners use indoor trainers safely?
Absolutely. Most trainers support low resistance and stable mounting for new riders.
Is indoor cycling good for joints?
Yes. Cycling is low-impact and gentle on knees and hips when adjusted correctly.
Conclusion
Indoor cycling offers control, consistency, and measurable progress. With thoughtful selection, proper setup, and regular use, a trainer becomes a long-term fitness investment. Riders who choose the Best Cycle Trainer gain freedom from weather, traffic, and schedule limits while improving health and performance year-round.
A smart choice today creates stronger rides tomorrow.
Health
EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator: Efficient Home Oxygen System
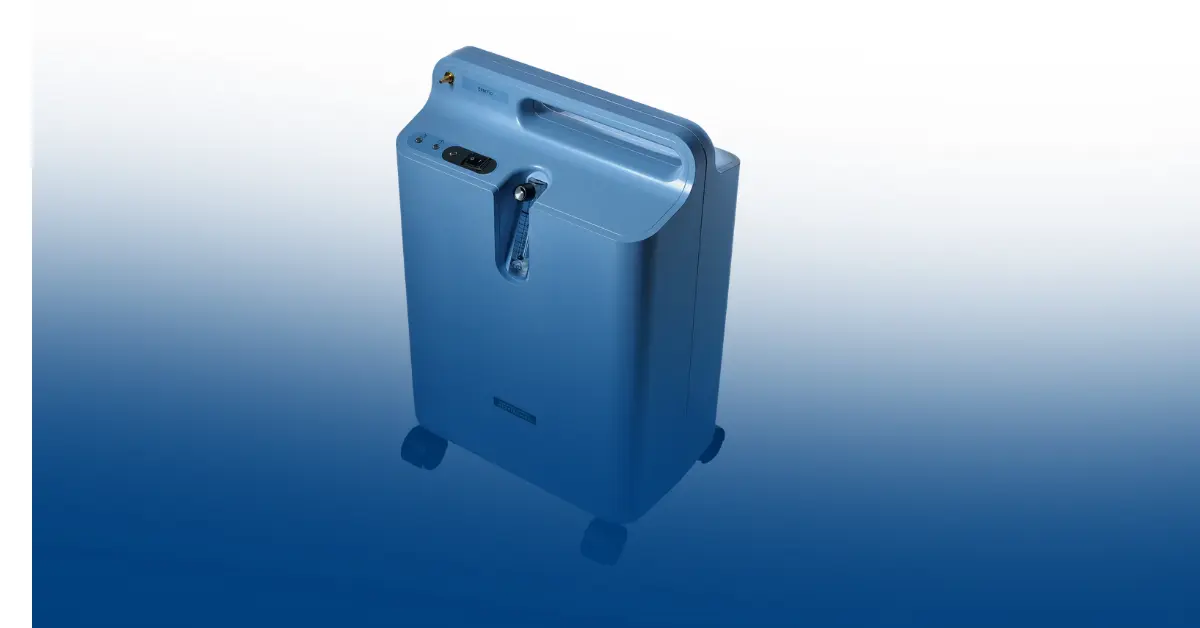

Table of Contents
Introduction
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator has earned a strong reputation as one of the most efficient and user-friendly home oxygen therapy devices on the market. Manufactured by Philips Respironics, it’s designed to offer patients consistent oxygen flow while minimizing noise, energy consumption, and maintenance needs.
If you’re seeking a compact, dependable, and affordable oxygen solution, the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator stands out for its simplicity and long-term reliability.
What Is the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator?
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator is a stationary medical device that separates oxygen from ambient air and delivers high-purity oxygen to patients with respiratory conditions such as COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), asthma, or emphysema.
For a guide on nvacare Oxygen Concentrator click here
Unlike oxygen cylinders, it does not require refills. Instead, it extracts oxygen from the air continuously, providing an unlimited supply as long as it’s powered on. This makes the EverFlo model both cost-effective and low-maintenance for patients relying on home oxygen therapy.
Key Features of EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator
Philips designed the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator to meet modern healthcare standards while keeping it simple and easy for home users. Here are its standout features:
- Compact and Lightweight: Weighs only 31 pounds, making it easy to move.
- Quiet Operation: Noise levels are below 45 decibels for peaceful sleep and comfort.
- Energy Efficient: Consumes only about 350 watts, reducing electricity costs.
- High Oxygen Purity: Provides 93% ±3% oxygen concentration for safe therapy.
- Durable Design: Long-life filters reduce the need for frequent servicing.
- Integrated Humidifier Bottle Holder: Adds comfort for patients needing moist oxygen.
Each feature of the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator reflects Philips’ focus on comfort, reliability, and sustainability in home oxygen delivery.
How Does the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator Work?
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator uses Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology to filter nitrogen and deliver purified oxygen. Here’s a simple explanation of the process:
- Air Intake: The device draws room air through its filter system.
- Filtration: Dust and particles are removed for cleaner air.
- Nitrogen Separation: Using zeolite sieve beds, nitrogen is separated from oxygen.
- Oxygen Delivery: Pure oxygen is delivered to the user through a nasal cannula.
The system ensures a steady supply of medical-grade oxygen without the need for cylinder replacements — one of the major advantages of the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator.
Benefits of Using the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator
Using the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator comes with numerous benefits that enhance both patient comfort and quality of life:
- Low Maintenance: No filter changes for up to two years.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Energy-efficient design saves on monthly bills.
- Portable for Home Use: Easy to move from one room to another.
- Quiet Functioning: Ideal for use during sleep or while watching TV.
- Environmentally Friendly: No cylinder refills or transport emissions.
These advantages make the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator a preferred choice for patients who value convenience and reliability in long-term oxygen therapy.
EverFlo vs. Other Oxygen Concentrators
When compared to other home oxygen systems, the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator has several competitive advantages:
| Feature | EverFlo | Invacare | AirSep VisionAire |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 31 lbs | 43 lbs | 30 lbs |
| Power Consumption | 350W | 410W | 290W |
| Noise Level | <45 dB | 50 dB | 45 dB |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Warranty | 3 years | 3 years | 2 years |
This comparison highlights that the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator provides an excellent balance of lightweight design, efficiency, and quiet operation, making it ideal for most home-based patients.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
To ensure long-term performance, users should follow these maintenance and safety tips for their EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator:
- Keep the device away from walls to maintain airflow.
- Replace or clean filters as recommended.
- Avoid smoking or open flames near the unit.
- Use distilled water in the humidifier bottle.
- Schedule professional service every 12 months.
Routine maintenance not only extends the device lifespan but also guarantees consistent oxygen purity and safe operation.

Where to Buy the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator
You can purchase the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator through several trusted medical suppliers and online platforms such as:
- Philips Respironics Authorized Dealers
- RehabMart
- Vitality Medical
- Medical Supply Depot
- Amazon (with verified medical sellers)
Always ensure you’re buying from a certified dealer to receive warranty support and genuine parts.
Customer Reviews and Expert Insights
Healthcare professionals praise the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator for its reliability, simplicity, and minimal upkeep. Patients often highlight its:
- Low noise output
- Compact design
- Energy savings
- Continuous oxygen flow
Experts also note that Philips’ use of long-lasting filters and durable internal components contributes to fewer breakdowns, which is especially valuable for patients needing 24-hour oxygen therapy.
Technical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Oxygen Flow | Up to 5 LPM |
| Oxygen Concentration | 93% ±3% |
| Power Consumption | 350W |
| Sound Level | ≤45 dB |
| Weight | 14 kg (31 lbs) |
| Dimensions | 23” H x 15” W x 9.5” D |
| Warranty | 3 years |
These specifications show why the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator is among the most efficient and quiet oxygen systems for residential use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long can I run the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator?
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator is designed for continuous use and can operate 24/7 with proper ventilation.
2. Does it require distilled water?
Yes, if using the humidifier attachment, always fill it with distilled water to avoid mineral buildup.
3. Is it noisy?
No, it operates below 45 decibels—quieter than most home concentrators.
4. How often should I service it?
It requires professional service once a year or as recommended by Philips.
5. Can I travel with this device?
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator is a stationary model, not portable, but easy to move around your home.
Conclusion
The EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator by Philips Respironics represents a perfect blend of performance, reliability, and user comfort. Its low maintenance design, quiet operation, and energy efficiency make it one of the best home oxygen therapy systems available today.
For patients who need continuous oxygen support without constant cylinder replacements, the EverFlo Oxygen Concentrator is a dependable, cost-effective, and long-lasting solution.
Health
Invacare Oxygen Concentrator: Reliable Home Oxygen Solution
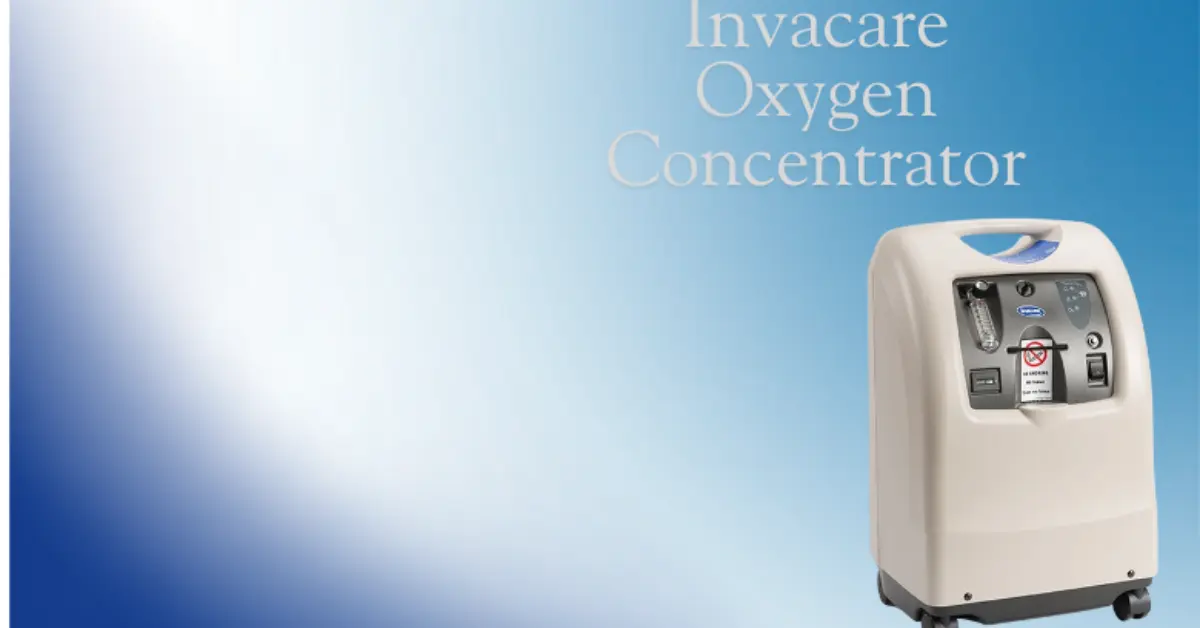
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to home oxygen therapy, few names are as trusted as the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator. Designed with advanced technology and patient comfort in mind, Invacare has established itself as a global leader in respiratory care equipment. This article explores how Invacare’s devices deliver reliability, efficiency, and value for patients requiring continuous oxygen therapy.
What Is an Invacare Oxygen Concentrator?
An Invacare Oxygen Concentrator is a medical device that extracts oxygen from the surrounding air and delivers it to users with respiratory conditions like COPD, emphysema, or chronic bronchitis. Unlike oxygen tanks that require frequent refills, concentrators provide an endless oxygen supply as long as they remain plugged in.
Invacare’s models are engineered to offer quiet operation, energy efficiency, and enhanced mobility—making them a top choice for both home and clinical environments.
Key Features of Invacare Oxygen Concentrators
Invacare offers multiple models such as the Invacare Perfecto2 V and Invacare Platinum 10, each packed with innovative features. Some key highlights include:
- Continuous Flow Oxygen: Provides consistent oxygen output up to 10 liters per minute.
- Low Noise Operation: Advanced compressor design minimizes sound for peaceful home use.
- Energy Efficient: Uses minimal power, reducing electricity costs.
- Easy Maintenance: Designed for user-friendly filter replacement and cleaning.
- Built-In Alarms: Alerts for low oxygen purity, high temperature, or power issues.
Each feature of the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator aims to make long-term oxygen therapy safer and more comfortable.
How Does the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator Work?
The device works through Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology, separating nitrogen from ambient air and delivering oxygen-enriched air through a nasal cannula or mask. The Invacare Oxygen Concentrator continuously monitors oxygen purity to ensure optimal performance.
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Air Intake: The unit draws in surrounding air.
- Filtration: Removes dust and impurities.
- Oxygen Separation: Nitrogen is filtered out using zeolite sieve beds.
- Delivery: Pure oxygen is supplied to the user through tubing.
This self-sustaining system ensures patients receive high-purity oxygen without refilling tanks or cylinders.
Top Invacare Oxygen Concentrator Models
1. Invacare Perfecto2 V
- Compact, lightweight design
- Delivers up to 5 LPM (liters per minute)
- Energy Star rated for efficiency
- Ideal for home users needing moderate oxygen support
2. Invacare Platinum 10
- Heavy-duty concentrator with up to 10 LPM output
- Features top-grade filtration and durability
- Suitable for hospitals or patients requiring higher oxygen flow
Both models reflect Invacare’s commitment to combining medical-grade performance with user-friendly functionality.
Benefits of Using an Invacare Oxygen Concentrator
Using an Invacare Oxygen Concentrator offers several life-enhancing advantages:
- Reliable Oxygen Supply: Eliminates the need for cylinder refills.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces long-term expenses compared to oxygen tanks.
- Mobility Options: Compatible with portable oxygen devices.
- Enhanced Safety: Built-in sensors ensure purity and performance.
- Eco-Friendly: Uses air instead of disposable cylinders.
These benefits make Invacare devices a preferred choice among patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
To ensure your Invacare Oxygen Concentrator performs at its best:
- Clean or replace filters regularly (as per the manual).
- Keep the unit in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid placing it near open flames or smoke.
- Check tubing for leaks or kinks.
- Schedule annual service by an authorized technician.
Routine care extends device lifespan and ensures uninterrupted oxygen therapy.
Where to Buy Invacare Oxygen Concentrators
You can purchase the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator through:
- Authorized dealers listed on the Invacare official website.
- Medical supply retailers such as Rehabmart and Vitality Medical.
- Healthcare providers who supply equipment through insurance programs.
Always verify the product authenticity and warranty when purchasing online or through third-party sellers.
Customer Reviews and Expert Insights
Patients praise the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator for its:
- Long lifespan
- Quiet operation
- Easy maintenance
- Reliable oxygen output
Respiratory therapists often recommend Invacare due to its stable performance and FDA-approved safety standards. These factors contribute to its reputation as a hospital-grade product trusted for home use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does an Invacare Oxygen Concentrator last?
Most models last between 5–7 years with proper maintenance and care.
2. Can I travel with an Invacare Oxygen Concentrator?
Yes. Invacare offers portable concentrators designed for travel, complete with rechargeable batteries.
3. How often should I service my concentrator?
It’s recommended to get the device professionally serviced once a year for optimal performance.
4. Does it work during power outages?
You’ll need a backup oxygen source or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to ensure continuous use.
5. Is it covered by insurance?
Many healthcare insurance plans cover Invacare Oxygen Concentrators when prescribed by a physician.
Conclusion
The Invacare Oxygen Concentrator stands out as a reliable, efficient, and medically certified oxygen therapy solution for patients needing consistent respiratory support. Whether you choose the Perfecto2 V for home use or the Platinum 10 for clinical settings, Invacare ensures superior performance, safety, and peace of mind.
By combining advanced technology with user comfort, the Invacare Oxygen Concentrator continues to redefine what home oxygen therapy can be — a seamless, secure, and life-improving experience.
-

 Must Read6 months ago
Must Read6 months agoThe Truth Behind the Direct Fairways Lawsuit: What You Need to Know
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoTop Chartered Accountants Benefits: Guide, Tips, FAQs & More
-

 Tech7 months ago
Tech7 months agoblogsternation .com: Complete Beginner’s Guide, Benefits, and FAQs
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoHow to Upgrade Graphics Driver: Boost Speed, Fix Issues & Enhance Gaming
-

 Sports7 months ago
Sports7 months agoHow Many Quarters in Football? A Complete Guide to Game Structure and Timing
-

 Education7 months ago
Education7 months agoOxford Acceptance Rate: What It Means, Why It Matters, and How to Beat It
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoUnlocking the Truth About gomyfinance.com Credit Score
-

 Editors Pick6 months ago
Editors Pick6 months agoAstonishing Mist: Why Delta Flight DL275 Diverted LAX Mid‑Pacific



















